Table of Content
Regulatory Requirements of Food for Infant Nutrition as Per FSSAI

Summary
- Infant nutrition should meet age, texture and taste requirements.
- Labels should include clear nutritional information regarding the formulation.
- Microbiological and contaminant limits are to be strictly adhered to.
- Advertising must be truthful and comply with regulatory requirements.
- The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) certification is mandatory for manufacturing and selling infant food.
Short Description
This article outlines the important Food Safety and Standards governing infant nutrition; including general requirements, labelling, microbiological standards, contaminants and advertising guidelines.
General Requirements for Infant Nutrition
Foods for infants must adhere to specific guidelines regarding age-appropriateness, texture and taste. These products should be designed to cater to the nutritional needs of infants and should be composed of only approved ingredients and textures suited for different developmental stages. General requirements include:
- Age Group: The infant formula is tailored to infants up to 6 months old. Follow-up formula is for infants aged 6-24 months and is designed to be the liquid part of their diet.
- Texture: Must be smooth, uniform in appearance and free from lumps.
- Taste: It should be free from musty odour and rancid taste and suitable for infant taste buds.
- Ingredients: Should be based on milk of cow, buffalo, or other milch animals or a blend along with additional nutrients and ingredients specified in these regulations.
Labelling Requirements as per the Food Safety and Standards Act (FSS) and 2020 Regulations
Proper labelling is essential for infant foods as it provides crucial information to parents and caregivers. Labels must include the name of the food, ingredients, nutritional content, additives, recommended age group and preparation instructions.
Additionally, labels should comply with the FSS (Foods for Infant Nutrition) Regulations and the Food Safety and Standards (Labelling and Display) Regulations, 2020. Some key points to consider in the labelling:
- Ingredient List: Must include all components in descending order of quantity.
- Nutritional Components: Should detail key nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and energy content.
- Indication of Vegetarian or Non-vegetarian: Labels should include logos to specify this.
- Food Additives Declaration: Only the food additives listed under the regulations shall be used and given on the label with their specific name and appropriate class title in the ingredients list.
- Others: The name and address of the brand owner, the FSSAI logo and license number, net quality, retail sale price, the date of manufacture and expiry, and BIS Certification Marking should be included in the food label. Additionally, the country of origin and possible allergens present must also be declared.
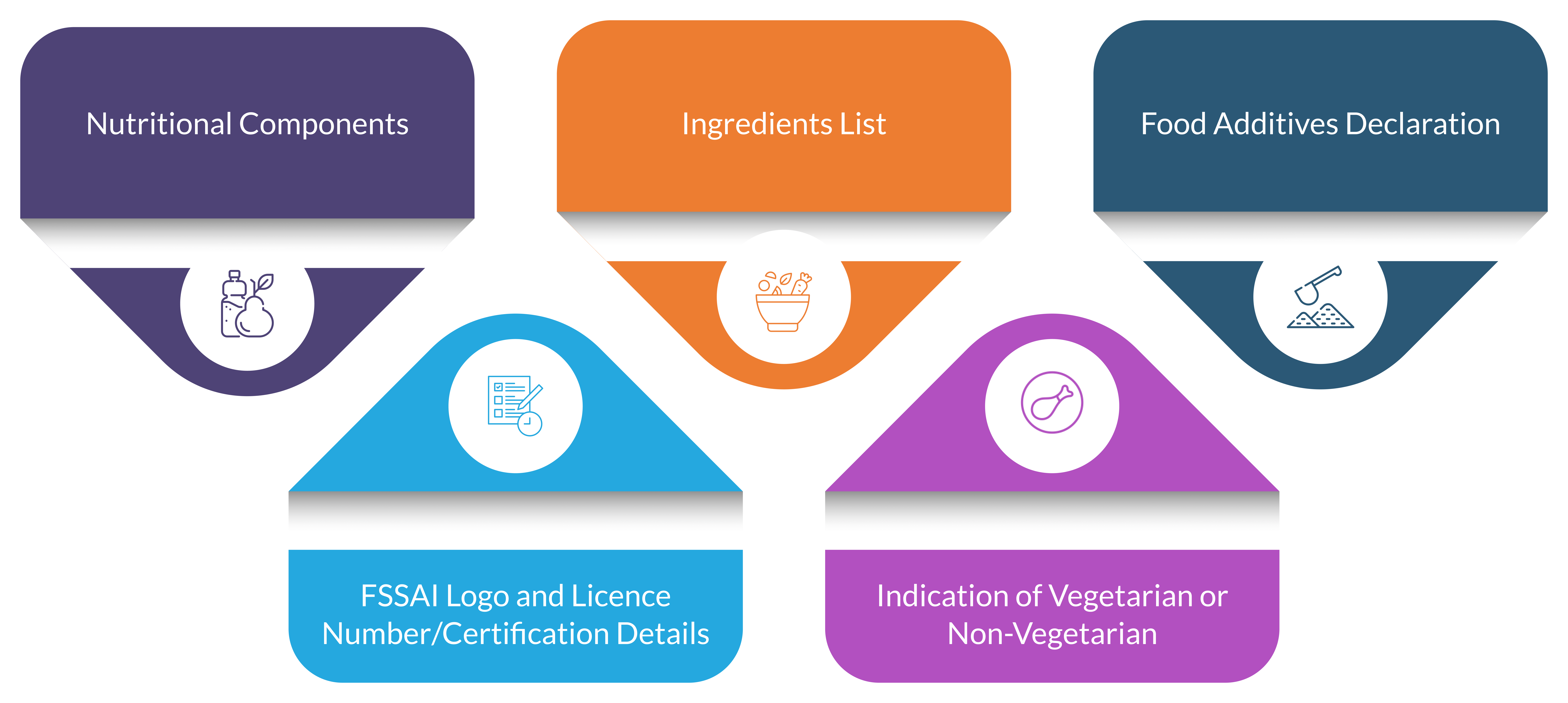
Fig 1: Key Points to Consider in a Label
Microbiological Requirements for Infant Nutrition
According to Appendix B of the Food Safety and Standards (Food Products Standards and Food Additives) Regulations, 2011, infant food should meet stringent microbiological standards to ensure they are free from harmful bacteria and pathogens.
Regular testing and compliance with these standards are critical to maintaining the safety of these products. Key microbiological standards include:
- Aerobic plate count: Should be within safe limits as specified by FSSAI.
- Coliforms and E. coli: Must be absent to prevent contamination.
- Salmonella and Listeria: Products must be free from these dangerous pathogens.
Additionally, for infant milk food, formula, and milk substitutes, Enterobacteriaceae bacteria must be tested.
Heavy Metals and Other Contaminants Regulation
The presence of heavy metals, contaminants or toxic substances in infant food is strictly regulated under the Food Safety and Standards (Contaminants, Toxins, and Residues) Regulations, 2011.
These regulations enlist the allowed levels of substances such as lead, cadmium, copper, mercury, and arsenic in infant food to protect infants’ health. Key points regarding such contaminants are summarised in Table 1:
| Contaminant | Maximum Permissible Level |
|---|---|
| Lead | 0.02 mg/kg |
| Copper | 15 mg/kg (minimum 2.8 mg/kg) |
| Cadmium | 0.1 mg/kg |
| Arsenic | 0.05 mg/kg |
| Tin | 5 mg/kg |
Table 1: Allowed Limits for Contaminants in Infant Food
Other heavy metals and contaminants are to be strictly regulated to ensure no exposure to infant food.
Advertising and Claims Regulations Regarding Infant Products
Advertising of infant products must be carefully regulated to prevent misleading claims and ensure compliance with the Food Safety and Standards (Advertising and Claims) Regulations, 2018. Additionally, the Infant Milk Substitutes, Feeding Bottles, and Infant Foods (Regulation of Production, Supply, and Distribution) Act, 1992, governs the marketing and promotion of these products.
Key points to keep in mind when promoting these products include:
- No Misleading Claims: It is illegal to suggest or imply that these products are equal to or better than mother’s milk. Truthful advertisement based on clauses under the Infant Milk Substitutes, Feeding Bottles, and Infant Foods (Regulation of Production, Supply, and Distribution) Act, 1992 must be ensured.
- Clear Labelling: All containers must include labels with an “important notice” that is clear, easy to read, and understandable.
- Mandatory Statements: Labels must state that “mother’s milk is best for your baby,” in capital letters and warn that infant milk substitutes or foods should only be used on the advice of a health worker.
- Compliance with the IMS Act: Marketing must adhere to the guidelines set out in the IMS Act to avoid unethical promotion.

Fig 2: Important Provisions for Advertising Infant Products
BIS Certification for Manufacturing and Sale
Ensuring the safety and quality of infant nutrition products is crucial for the well-being of small children. The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) Certification plays a vital role in upholding this standard stated under the Food Safety and Standards (Prohibition and Restrictions on Sales) Regulations, 2011.
It states that no person is permitted to manufacture, sell, store, or exhibit food for infant nutrition without the BIS Certification Mark, wherever BIS standards are available. This certification ensures that products meet the necessary safety and quality standards.
Conclusion
To ensure the highest standards of quality and safety for infant nutrition strict adherence to comprehensive guidelines is essential. From age-suitable formulations and specific texture and taste requirements to strict labelling, microbiological, and contaminant regulations, every detail is important for protecting infant health.
Along with proper advertising and claims regulations, obtaining BIS certification guarantees that products meet high safety and quality standards. By following these regulations, manufacturers and sellers can ensure they are providing safe, nutritious, and well-regulated options for infants, supporting their healthy growth and development.
References:
- Food Safety and Standards (Foods for Infant Nutrition) Regulations, 2020 (https://www.fssai.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/Comp_IFR_VERSION-II_04_01_2024.pdf)
- Food Safety and Standards (Labelling and Display) Regulations, 2020 (https://www.fssai.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/Comp_Labelling.pdf)
- Appendix B microbiological requirements. Food Safety and Standards Regulations, 2011 https://fssai.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/Appendix%20B.pdf
- Food Safety and Standards (Contaminants, Toxins and Residues) Regulation, 2011 (https://www.fssai.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/Compendium_Contaminants_Regulations_28_01_2022.pdf)
- Infant Milk Substitutes, Feeding Bottles, and Infant Foods (Regulation of Production, Supply, and Distribution) Act https://www.bpni.org/docments/IMS-act.pdf
- Food Safety and Standards (Prohibition and Restriction of Sales) Regulation, 2011 (https://www.fssai.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/Comp_Prohibition%20and%20Restrcition%20of%20sales%20X_03_04_2023.pdf)
Enquire Now
To enquire about our services please complete the form below and we will be in tough with you as soon as possible
Food Regulatory Services
- Consumer Product
- Compliance Services
- Licenses